Fabrication of Ultrasound Transmitter and Receiver for Biomedical Imaging
Ultrasound based imaging devices for assistance in medical surgery. Involves development of an ultrasound imaging assisted brain cannula for improved accuracy of the cannula reaching a ventricle (fluid filled cavity) in the brain.
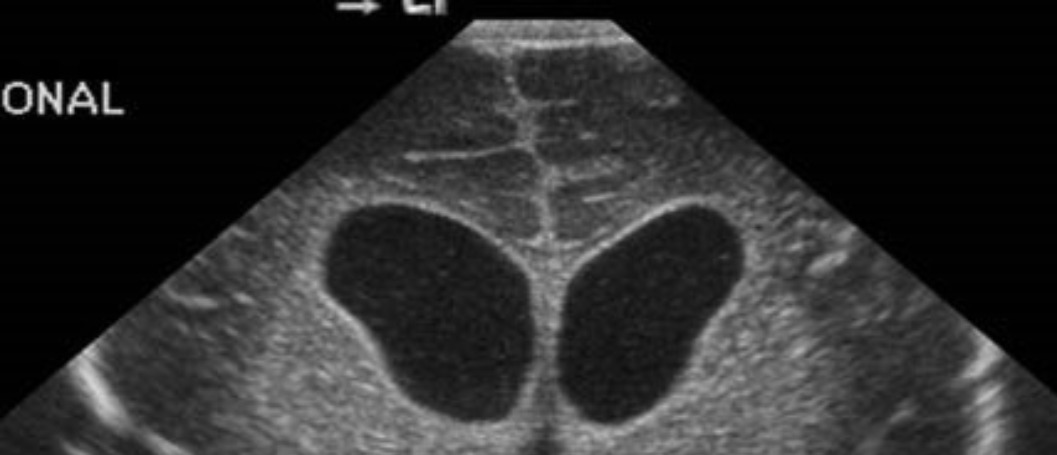


This project involves development of ultrasound based imaging devices for assistance in medical surgery. One example is the development of an ultrasound imaging assisted brain cannula for improved accuracy of the cannula reaching a ventricle (fluid filled cavity) in the brain. An ultrasound reflection (echo) based imager is envisaged for this. Another application is reflection AND transmission mode in which images in both modes are fused together for better image signal-noise ratio. One difficulty with research related to ultrasound based devices is that the transducers are (a) not easily available in the market (b) are typically very expensive and (c) do not have standardized mechanical or electrical interfaces. Apart from biomedical imaging ultrasound transducers are also useful in identifying cracks/defects in materials. This makes the area of ultrasonic transducers very important and strategic with several application dimensions including biomedical imaging for diagnosis. One basic work is understanding, simulating and measuring ultrasound wave propagation across well-defined material interfaces under ideal conditions. Preliminary work on simulation of ultrasound transmission using SPICE simulator was done based upon the work of Deventer[Deventer] and the SPICE models developed by Ilich[Ilich]. Subsequently an ultrasound transmitter and receiver was conceived and designed. The current phase of the work is on developing the hardware board and testing it with different materials including materials which will mimic human tissues. The circuits include oscillators, drivers to drive the very low impedance of the piezo-electric transducer and amplifiers to detect the weak echoes received by the transducer.
Principle Investigators
Team Members